17 soap ingredients that could trigger eczema in kids
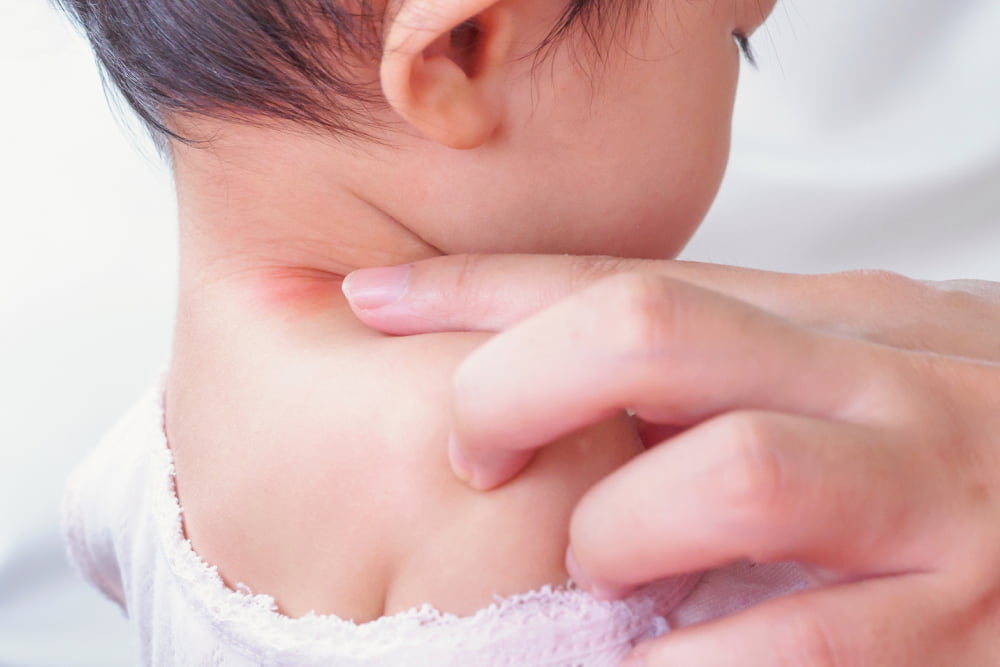
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic skin condition characterized by patchy and scaly skin. Statistical data suggests that the condition affects around 9.6 million children nationwide. Managing eczema’s symptoms can be challenging, but one often overlooked aspect is the choice of soap. Certain soap ingredients can exacerbate eczema symptoms in children, causing increased discomfort. This article provides an insight into common soap ingredients that can aggravate eczema in children and suggests gentler alternatives:
Understanding eczema in children
Before delving into specific soap ingredients, it is essential to understand the nature of eczema in children. Eczema is characterized by dry, itchy skin, redness, and inflammation. It can vary in severity, with some children experiencing occasional flare-ups and others dealing with constant discomfort. The condition often begins in infancy and can persist into adulthood.
Common soap ingredients to avoid
Fragrances
Fragrances are added to many soaps to enhance their appeal. However, these artificial scents can contain a mix of chemicals that irritate sensitive skin. For children with eczema, fragrance-free or hypoallergenic soaps are the safer choice.
Sulfates
Sulfates, such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), are common surfactants in soaps and shampoos. Though they create a rich lather, sulfates can strip the skin of its natural oils and compromise the skin barrier. It is better to choose sulfate-free alternatives that can protect a child’s delicate skin.
Parabens
Parabens are preservatives that extend a product’s shelf life. Some studies suggest they might be linked to skin irritation and allergies, making them potential eczema triggers. Choosing paraben-free soap can reduce the risk of skin irritation.
Dyes and colorants
The vibrant colors in some soaps come from synthetic dyes and colorants. Unfortunately, these additives often contain harsh chemicals that irritate sensitive skin. To minimize the risk of eczema flare-ups, consider clear or naturally colored soaps without synthetic dyes.
Essential oils
While some essential oils can be soothing for the skin, others can be irritants for children with eczema. Ingredients like lavender, citrus oils (e.g., lemon, lime, orange), and mint oils (e.g., peppermint, spearmint) may be too harsh. Parents should exercise caution or choose hypoallergenic essential oil-free soap options.
Antibacterial agents
Soaps with antibacterial agents like triclosan can disrupt the natural balance of skin bacteria and contribute to dryness and irritation, potentially worsening eczema symptoms. Forgo antibacterial additives unless recommended by a healthcare professional.
Formaldehyde-releasing preservatives
Some soaps contain preservatives that release formaldehyde over time to extend shelf life. Formaldehyde can be a skin irritant and allergen, potentially exacerbating eczema. Parents should look for soaps labeled as formaldehyde-free.
Propylene glycol
This ingredient, commonly found in personal care products, can cause skin irritation and may be unsuitable for kids with eczema. It is best to opt for soap without propylene glycol or other potentially irritating glycols.
Artificial emollients
While emollients are often added to soap for their moisturizing benefits, artificial emollients can sometimes contain irritants. Look for soaps with natural, gentle emollients like shea butter, cocoa butter, or aloe vera.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) and methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI)
These preservatives are known allergens and skin irritants. They are often found in personal care products, including soaps. One must opt for MI/MCI-free soap products to reduce the risk of skin irritation.
Mineral oil
Some soaps may contain mineral oil, which, while it can lock in moisture, might also be comedogenic (tending to clog pores) for some individuals. This can lead to skin irritation and worsen eczema symptoms. One should consider soap alternatives without mineral oil.
Alkali ingredients
Soaps with a high pH level (alkaline) can disrupt the skin’s natural pH balance, leading to dryness and irritation. Thus, it is advisable to choose a soap with a balanced pH closer to the skin’s natural pH to help maintain skin health.
Retinoids
Some specialty soaps, especially those marketed for acne treatment or anti-aging purposes, may contain retinoids like Retin-A or Retinol. These can be harsh for sensitive skin and may worsen eczema. Thus, it is important to avoid soaps with retinoid ingredients for children with eczema.
Lanolin
Lanolin, derived from sheep’s wool, is often added to soaps and skincare products for its moisturizing properties. However, it can be a potential allergen and may lead to skin irritation in children with eczema. It is advisable to choose lanolin-free soap alternatives.
Salicylic acid
Some soaps, especially those designed for acne-prone skin, contain salicylic acid. This ingredient can be too harsh for sensitive skin, leading to dryness and exacerbating eczema symptoms. One should avoid soaps with salicylic acid for children with eczema.
Petrochemicals
Some soaps may contain petrochemicals derived from petroleum, such as mineral oil or petroleum jelly. These ingredients can create a protective layer on the skin, which may prevent moisture loss but can also be heavy and occlusive, potentially leading to skin irritation or worsening eczema symptoms. It is important to consider soap products without petrochemicals for children with eczema.
Phthalates
Phthalates are often used as plasticizers and can sometimes be found in fragrances and other additives in soap. They have been associated with skin irritation and allergic reactions. Therefore, it is advisable to choose soap options that are free of phthalates to reduce the likelihood of skin irritation in children with eczema.
Parents and caregivers of children with eczema must pay close attention to the soap products they choose. Avoiding soap ingredients known to be potential triggers can help minimize skin irritation and discomfort in young eczema sufferers. Selecting hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and gentle cleansers that are formulated for sensitive skin is crucial. Additionally, consulting a pediatric dermatologist or healthcare provider for personalized recommendations can assist in effectively managing eczema and ensuring the best care for a child’s skin. By making informed choices about soap, parents can play a vital role in helping their children find relief from eczema symptoms.





